The Endocannabinoid System
Human beings have been using cannabis for its medicinal and psychoactive properties for thousands of years, but there’s always been a veil over information regarding how and why cannabis works so well with treating such a wide variety of medical conditions. For decades, we have known that cannabis can be very helpful in treating glaucoma by lowering the intraocular pressure of the eye, which means that it can lower the fluid pressure and prevent optic nerve damage. But how does it work?
Endocannabinoids
Endogenous cannabinoids are a family of bioactive lipids that interact with and activate Endocannabinoid receptors via neural transmission. The brain and other tissues throughout the body contain naturally formed cannabinoids that regulate functions such as pain perception, memory, mood, and appetite in a homeopathic manner. One event that triggers the natural production of cannabinoids in your body is the Noxious Stimulus, a potentially or actually tissue-damaging event. When an event triggers your body, it synthesizes cannabinoids on-demand and releases them to activate presynaptic cannabinoid receptors in specific areas.
Endocannabinoid Receptors
Decades after the discovery of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the major psychoactive ingredient in cannabis which was first isolated in 1964 by Raphael Mechoulam and Yechiel Gaoni, the identification and successful cloning of the first cannabinoid receptor (CB1) came, and shortly after, cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Endocannabinoid System is not that simple.
- Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) receptors are thought to be one of the most widely expressed Gαi protein-coupled receptors in the brain. CB1 receptors have shown particularly high levels of expression in cortex, basal ganglia, hippocampus, cerebellum, and low levels of expression in brainstem nuclei. Also found in the medulla oblongata and spinal cord.
- CB2 receptors are mainly expressed on T cells of the immune system, on macrophages and B cells, and in hematopoietic cells. They also have a function in keratinocytes and are also expressed on peripheral nerve terminals. These receptors play a role in antinociception or the relief of pain. Activation of peripheral CB2 receptors generates an antinociceptive response in situations of inflammatory hyperalgesia and neuropathic pain.
Interaction between Cannabinoids and Receptors
Cannabinoid receptors are Gi/o-protein-coupled receptors anchored in the cell membrane and can be found throughout most of the body’s systems. So how do Cannabinoids interact with their host receptors? Here’s an example below. More facts about the Endocannabinoid System.
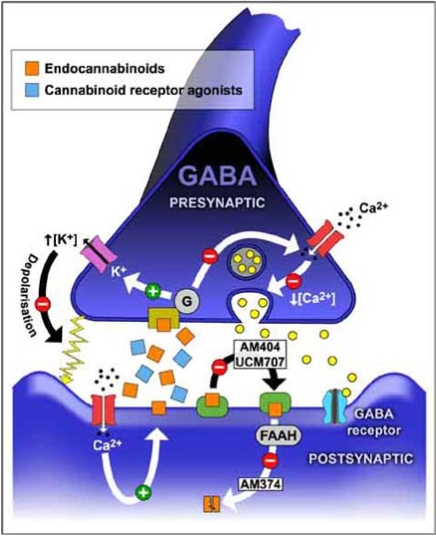
The major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system is gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The image displays a GABA neurotransmitter synapse with CB1 receptors as therapeutic targets. Neurons synthesize endocannabinoids which activate presynaptic CB1 receptors in the synaptic space. Pharmacological methods such as administering agonists or inhibiting reuptake or degradation of endocannabinoids can enhance cannabinoid receptor activity.
Cannabinoids alter neuron communication and have untapped medical potential. Studying different cannabinoids and receptors may advance pain management, neuroprotection, motor control (e.g., Parkinson’s), spinal injury, weight control, anxiety, neuropathy, glaucoma, nausea, emesis, and wasting diseases. Research has shown promise in treating inflammation, cancer, epilepsy, PTSD, depression, gastrointestinal disease, traumatic brain injury, and stroke. The list goes on and on.
Cannabis has an exciting future ahead of it, and the science behind it is finally becoming unveiled!
Check out Our Latest Promotions